Guanidine hydrochloride is
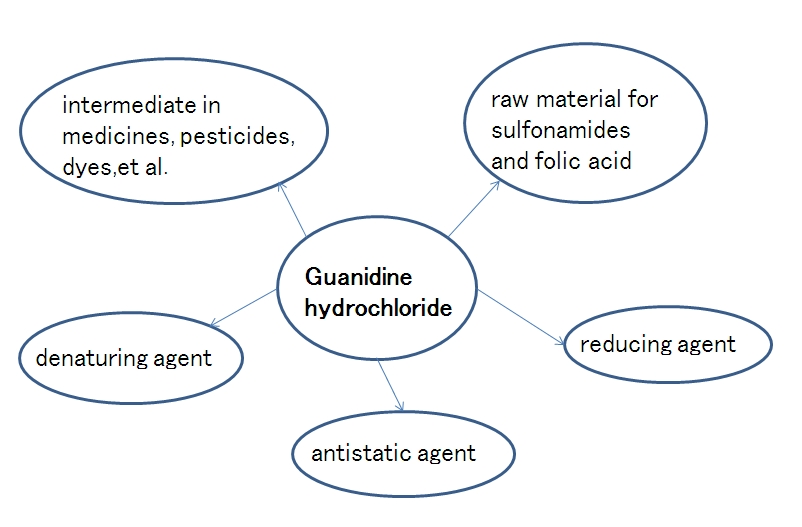
often used as an intermediate in medicines, pesticides, dyes and other
organic compounds, it is also an important raw material for sulfonamides
and folic acid; it can be used as a strong denaturants in the
extraction of total RNA from cells. The proportion of traditional
refined guanidine hydrochloride synthetic preparation process is simple,
and the operation in each process is not strict: such as mixing
impurities during stirring, temperature is difficult to observe, and
weighing is inaccurate. Both of them lead to the problem that the low
purity of the Guanidine HCL and the incomplete reaction. Then how to solve these problems?
Researchers
have developed a new guanidine hydrochloride synthetic preparation
process, which solves the shortcomings of the prior part. As a
preference, the following steps are included:
1.
Ratio: (1) dicyandiamide 350g, ammonium chloride 450g, ammonium
carbonate 50g, (2) dicyandiamide 168g: ammonium chloride 203g: ammonium
carbonate 19g; weighting by electronic precision balance, one
prefabricated, another reserved.
2.
Preparation, adding the pre-formed raw materials to the reaction kettle
with electric heating function, adding the spare raw materials to the
porcelain quality cup (high-temperature disinfection after washing and
drying before operation), and uniformly stirring the raw materials in
reaction kettle through the non-front glass rod. The raw materials in
the porcelain cup are are added to the reaction kettle after the raw
materials in that are uniformly stirred;
3, heating, the reactor is heated to 170°C±5°C, and monitored by a temperature sensor;
4. The synthesis reaction is carried out in a reactor environment of 170°C±5°C for three hours;
5. Preparation was completed, and the reaction vessel was opened to obtain 385 g of hydrazine hydrochloride.
The
preparation process not only has a precise ratio, the reaction
temperature is convenient for observation and control, no impurity is
mixed during stirring, the reaction is complete, and the prepared
guanidine hydrochloride is also high in purity.
Edited by Suzhou Yacoo Science Co., Ltd.
2019年3月13日星期三
2018年9月7日星期五
Preparation Of Graphene Using Guanidine Hydrochloride As Reducing Agent
Guanidine hydrochloride,
which is often used as an intermediate in medicines, pesticides, dyes
and other organic compounds, is an important raw material for
sulfonamides and folic acid; it can be used as a strong denaturants in
the extraction of total RNA from cells, and used for denaturation and
complexation of proteins. It can be used as an antistatic agent for
synthetic fibers. In addition, it can also be used as a reducing agent
to prepare graphene.
Graphene
is a two-dimensional crystal composed of carbon atoms with only one
layer of atomic thickness. It is an ultra-thin material with high
strength and toughness. It has a large breaking strength which is 200
times more than steel. It has 20% stretching range and excellent
electrical conductivity.
Due
to its unique quantum effect and excellent electrical, thermal and
mechanical properties, graphene has broad application in nanoelectronic
devices and integrated circuits, flexible electronic devices, ultra-high
sensitive sensor devices and other new electronic devices, composite
materials, solar cells, super capacitors, hydrogen storage materials,
etc.

The Existing Preparation Method
At
present, preparation methods of graphene mainly include physical
mechanical stripping method, vapor deposition method and chemical
method. Mechanical methods include micro-mechanical stripping methods,
epitaxial growth methods and heating of SiC. It is difficult to prepare
graphene with large area and uniformly thick.
Compared
with physical methods, chemical method for preparing graphene has a
high yield. It has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost
and large-scale production, and thus becomes a common method for
preparing graphene. However, in the reduction of graphene oxide, the
selected reducing agents are mainly hydrazine hydrate and its
derivatives, NaBH4, p-phenylenediamine, sulfur compounds, etc. Most of
the reducing agents are toxic and explosive, which is not conducive to
large scale production.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop a simple, efficient, low-cost and environmentally friendly method.
The researchers developed a method for preparing graphene with guanidine hydrochloride (CAS 50-01-1) as a reducing agent [1]:
(1)
Dispersing graphene oxide in water, treating with a cell disrupter for
20~90min and then continuing ultrasonic for 10~60min to obtain a
uniformly dispersed graphene oxide with a concentration of 0.1~10mg/mL;
(2)
Adding soluble polymer (one of polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyacrylamide,
polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, hydroxymethyl cellulose,
polyacrylic acid) to the graphene oxide dispersion, ultrasonic
dispersion 5~30min, a mixed solution of polymer and graphene oxide is
obtained, and the mass concentration of the soluble polymer in the mixed
solution is 0.01~0.1 mg/mL;
(3)
Adding guanidine hydrochloride to the above mixed solution, the mass
ratio of guanidine hydrochloride to graphene oxide is 10:1~100:1, and
adding alkaline solution (10%~28% ammonium hydroxide, 0.1~5mol/L NaOH
solution, 0.1~5mol/L KOH solution) to adjust the pH to 8~12, stir in the
oil bath (60~100°C), the reaction time is 1~5h. The water-soluble
graphene is obtained by centrifuging and washing.
The
preparation method has the advantages of simple preparation process,
low equipment requirement, and easy preparation of graphene in large
quantities; the presence of the soluble high molecular polymer greatly
improves the water solubility of the graphene, and is also beneficial to
the further preparation of the graphene film. Guanidine hydrochloride (Guanidinium chloride)
can be used as a reducing agent to prepare graphene which can be stably
dispersed in an aqueous solution, and the prepared graphene can be used
for constructing sensor and electrical device.
Reference
[1]
Ma Qi, Song Jinping, Guo Yong, et al. A method for preparing graphene
with guanidine hydrochloride as a reducing agent. CN104261393B, 29 June
2016.
Edited by Suzhou Yacoo Science Co., Ltd.
订阅:
博文 (Atom)