Tris(Hydroxymethyl) Aminomethane (TRIS) buffer
solution is a biological reagent, which is a buffer solution commonly
used in biological preparation and medical preparation. For example,
it’s commonly used in peprotech recombinant cytokines and protein
solubilization, and widely used as solvent for nucleic acid and proteins
electrophoresis. Usually, it is used as a liquid, but it is not easy to
store for a long time and the preparation is inconvenient. If it is
made into a tablet, the above problem will be well solved.
Some researchers have provided a preparation method of TRIS buffer tablets which are ready to use, easy to store, simple and quick to prepare. The steps are as follows:
(1) TRIS, boric acid, EDTA, cross-linked amylose (weight ratio:
54:22~23:3.0~3.5:3.3~4), pulverized to make into particles with 100~200
mesh; The main material trishydroxymethylaminomethane is in the grade of
pharmacopoeia; Excipients boric acid and EDTA are AR grade, crosslinked
amylose and microcrystalline cellulose are biological grade;
(2) mixing and stirring evenly;
(3) Tablet press, pressure 2~4 tons;
(4) Weighing and testing;
(5) Packaging.
The pH of the TRIS buffer
solution varies with temperature greatly, making it more difficult to
formulate the solution. The buffer tablet provided by the method is
simple and easy to use, and can be quickly opened and disintegrated as
long as the tablet is put into the quantitative water, thereby obtaining
a buffer solution with an accurate pH value, saving the user's manpower
and material resources and improving work efficiency. At the same time,
it is easy to store, carry and transport. The storage period is up to
3~5 years, and suitable for industrial production.
Edited by Suzhou Yacoo Science Co., Ltd.
2019年3月13日星期三
2018年11月2日星期五
Modification of zein functional drug-loaded microsphere with TRIS
As a common biological buffer, Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Aminomethane
(TRIS) is not only widely used as a solvent for nucleic acids and
proteins, but also as one of the main components of protein
electrophoresis buffers. It can also produce a variety of chemicals and
pesticides, pharmaceutical products, and it is an important intermediate
for the preparation of surfactants, vulcanization accelerators and some
drugs. This article will introduce another role of TRIS——modified zein
functional drug-loaded microspheres.
As
a natural hydrophobic macromolecule, zein has a wide range of sources,
it is non-toxic, non-immunogenic, and has good biocompatibility and
biodegradability. It is one of the few hydrophobic biopolymers that are
allowed to be taken orally by the FDA:
(1) Its
amino acid composition is very special, the proportion of non-polar
amino acids is more than 50%. It can embed various substances such as
polysaccharides. DNA, RNA, proteins, metal nanoparticles, quantum dots,
oil droplets, and hydrophobic drugs;
(2) The
amino acid residues on zein carry certain polar groups (such as ‐SH,
‐COOH, ‐NH3, and ‐OH), it provides the possibility to graft various
functional molecules for chemical reaction sites and adapt to the
complex and varied human environment.
Therefore,
zein is an advantageous drug carrier material. However, the proportion
of sulphur-containing amino acids in zein is only 2.8%, the ratio of
basic amino acids is only 2.9%, and the proportion of hydroxyamino acids
is 13.4%, which limits the selection of functional molecules and the
effect of modification. To improve this, the researchers modified it
with TRIS, including the following steps [1]:
(1)
The zein and the amino protecting agent di-tert-butyl dicarbonate are
dissolved in a specific dimethyl sulfoxide or ethanol aqueous solution
at a mass ratio of 1:1~1.5:1, and protected from light at 25~40°C. The
reaction is carried out for 12~24 hours to obtain a zein protection
solution;
(2) Under the protection of nitrogen, add carbodiimide salt, N-hydroxysuccinimide and TRIS (CAS 77-86-1) to the zein protection solution, and avoid the light reaction at 25-40°C for 12~24 hours. To obtain a TRIS-zein solution;
(3)
under the protection of nitrogen, adding concentrated hydrochloric acid
to the tris-zein solution, and avoiding light reaction at 25-40°C for
6-8h;
(4)
adjusting the pH to 5.0~6.0, transferring to a dialysis bag,
centrifuging the retained solution in the dialysis bag, and lyophilizing
to obtain TRIS-zein;
(5)
Dissolving the hydrophobic drug and the lyophilized TRIS -zein in an
aqueous solution of ethanol at a mass ratio of 1:1 to 1:10; and
injecting hydrochloric acid having a pH of 2.5 to 4.5 under magnetic
stirring. In the aqueous solution, after stabilization, the supernatant
is centrifuged to obtain a drug-loaded microsphere;
(6)
Functional modification of drug-loaded microspheres: separately prepare
solutions containing different functional molecules, disperse the
drug-loaded microspheres into a solution containing functional
molecules, stir the reaction, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and
obtain functional drug carrying microsphere. The drug microspheres have a
particle size of 100~300 nm and a drug-loading efficiency of
81.48~86.01%, and the grafting amount of the functional molecules is
1.72~1.94 times that of the unmodified zein microspheres.
The
coupling of TRIS to zein significantly improves the physicochemical
properties of zein. The prepared microspheres have good sphericity,
uniform particle size distribution, high drug-loading efficiency, and
are suitable for in vivo delivery. This research expands the application
of zein in drug delivery systems and has a good application prospect in
the field of medicine.
References
[1]
Jiang Yanbin, Pang Jiafeng, Lu Shan, Li Zhixian, Trimethylolamine
modified zein functional drug-loaded microspheres and preparation
method. 2018, CN108403662A.
Edited by Suzhou Yacoo Science Co., Ltd.
2018年10月12日星期五
TRIS, Bis-Tris, Tricine, TES, TAPS, What is the difference in application?
TRIS(Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Aminomethane),
Bis-Tris, Tricine, TES, TAPS are buffers commonly used in biochemical
experiments and molecular biology experiments, and they all contain the
structure of TRIS. Then what are the differences in application between
these buffers?
We hope that the following table could solve your doubts.
Table 1. The application of TRIS, Bis-Tris, Tricine, TES, TAPS
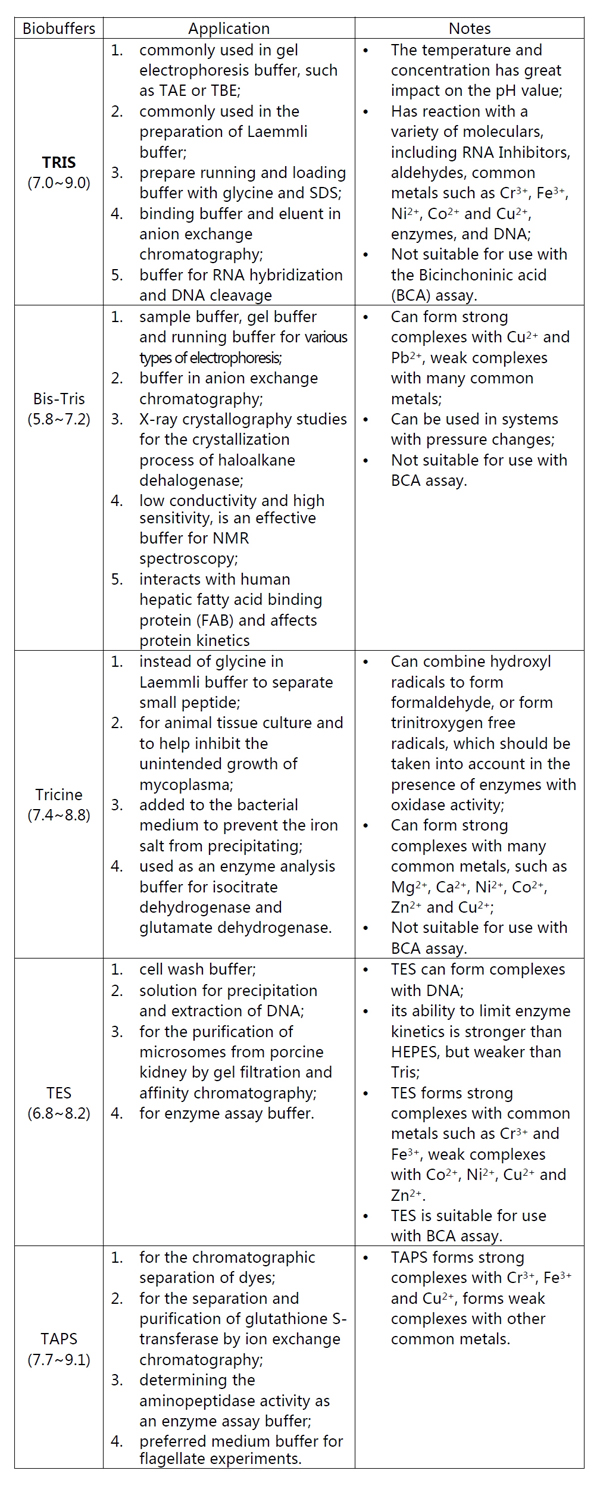
In specific use, buffers containing the TRIS (CAS:77-86-1)
structure will form a strong or weak complex with a variety of metal
ions, so the stability constant should be taken into account. In
addition, the buffer range and the appropriate type of experiment also
should be considered in order to obtain the best experimental results.
Edited by Suzhou Yacoo Science Co., Ltd.
订阅:
博文 (Atom)